All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Single, Double Or Secondary Glazing, Which Is The Best ... in Tapping WA
Glazing merely indicates the windows in your home, consisting of both openable and set windows, in addition to doors with glass and skylights. Glazing in fact simply indicates the glass part, however it is normally used to refer to all aspects of an assembly consisting of glass, movies, frames and home furnishings. Paying attention to all of these elements will help you to accomplish reliable passive design.
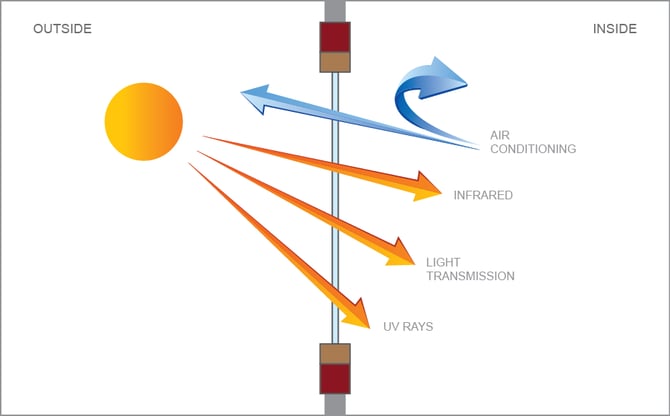
Energy-efficient glazing makes your house more comfortable and significantly minimizes your energy costs. Nevertheless, improper or improperly created glazing can be a significant source of unwanted heat gain in summer season and significant heat loss and condensation in winter. As much as 87% of a house's heating energy can be gained and as much as 40% lost through windows.
Which Type Of Double Glazed Window Frame Is Right For You? in Upper Swan WA
Glazing is a considerable financial investment in the quality of your house. The cost of glazing and the cost of heating and cooling your home are carefully associated. A preliminary financial investment in energy-efficient windows, skylights and doors can significantly decrease your yearly heating & cooling bill. Energy-efficient glazing also lowers the peak heating and cooling load, which can minimize the required size of an air-conditioning system by 30%, resulting in further expense savings.

This tool compares window choices to a base level aluminium window with 3mm clear glass. Understanding a few of the essential properties of glass will assist you to select the best glazing for your home. Secret residential or commercial properties of glass Source: Adjusted from the Australian Window Association The amount of light that passes through the glazing is referred to as noticeable light transmittance (VLT) or noticeable transmittance (VT).
Keeping Your House Cool In The Summer in Straffon Western Australia
This may lead you to turn on lights, which will result in higher energy costs. Conduction is how readily a product carries out heat. This is referred to as the U value. The U value for windows (revealed as Uw), describes the conduction of the whole window (glass and frame together). The lower the U worth, the higher a window's resistance to heat flow and the much better its insulating value.
If your house has 70m2 of glazing with aluminium frames and clear glass with a U value of 6. 2W/m2 C, on a winter's night when it is 15C chillier outside compared with inside, the heat loss through the windows would be: 6. 2 15 70 = 6510W That is comparable to the overall heat output of a large room gas heater or a 6.
What Are Double Glazed Windows? - Build in Rockingham Perth

If you choose a window with half the U value (3. 1W/m2 C) (for instance, double glazing with an argon-filled space and less-conductive frames), you can cut in half the heat loss: 3. 1 15 70 = 3255W The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) for windows (expressed as SHGCw) determines how easily heat from direct sunlight streams through a whole window (glass and frame together).
The lower a window's SHGC, the less solar heat it sends to the house interior. The actual SHGC for windows is affected by the angle that solar radiation strikes the glass.
Double Glazing Windows - The Best Installers In The Uk ... in Roleystone Western Australia
When the sun is perpendicular (at 90) to the glass, it has an angle of occurrence of 0 and the window will experience the maximum possible solar heat gain. The SHGC declared by glazing producers is constantly calculated as having a 0 angle of occurrence. As the angle increases, more solar radiation is shown, and less is sent.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Energy Efficient Windows At Everest in Lakes Perth
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in South Fremantle Western Australia
How Are Double Glazed Windows More Energy Efficient? in Safety Bay Western Australia
More
Latest Posts
Energy Efficient Windows At Everest in Lakes Perth
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in South Fremantle Western Australia
How Are Double Glazed Windows More Energy Efficient? in Safety Bay Western Australia