All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Insulated Glass Unit – Igu in Ashfield WA
Glazing just means the windows in your house, consisting of both openable and fixed windows, in addition to doors with glass and skylights. Glazing in fact just suggests the glass part, but it is generally used to refer to all elements of an assembly consisting of glass, movies, frames and home furnishings. Taking notice of all of these aspects will assist you to achieve effective passive design.

Energy-efficient glazing makes your home more comfortable and dramatically decreases your energy expenses. Unsuitable or inadequately created glazing can be a major source of undesirable heat gain in summer and significant heat loss and condensation in winter season. As much as 87% of a house's heating energy can be gained and up to 40% lost through windows.
Double-glazing Versus Low-e Glass in Floreat WA
Glazing is a substantial investment in the quality of your home. The cost of glazing and the expense of heating and cooling your home are carefully related. An initial financial investment in energy-efficient windows, skylights and doors can considerably reduce your annual heating & cooling costs. Energy-efficient glazing also minimizes the peak heating and cooling load, which can minimize the required size of an air-conditioning system by 30%, leading to more cost savings.

This tool compares window selections to a base level aluminium window with 3mm clear glass. Comprehending a few of the crucial properties of glass will help you to choose the finest glazing for your house. Key properties of glass Source: Adjusted from the Australian Window Association The quantity of light that travels through the glazing is called visible light transmittance (VLT) or visible transmittance (VT).
Lifestyle - West Coast Double Glazing in Kensington Western Australia
This might lead you to turn on lights, which will lead to greater energy costs. Conduction is how readily a material carries out heat. This is known as the U worth. The U worth for windows (revealed as Uw), explains the conduction of the whole window (glass and frame together). The lower the U value, the higher a window's resistance to heat flow and the better its insulating value.
If your home has 70m2 of glazing with aluminium frames and clear glass with a U value of 6. 2W/m2 C, on a winter season's night when it is 15C colder outside compared with inside, the heat loss through the windows would be: 6. 2 15 70 = 6510W That is equivalent to the total heat output of a large room gas heater or a 6.
Save Energy With Double Glazed Windows in Success Perth
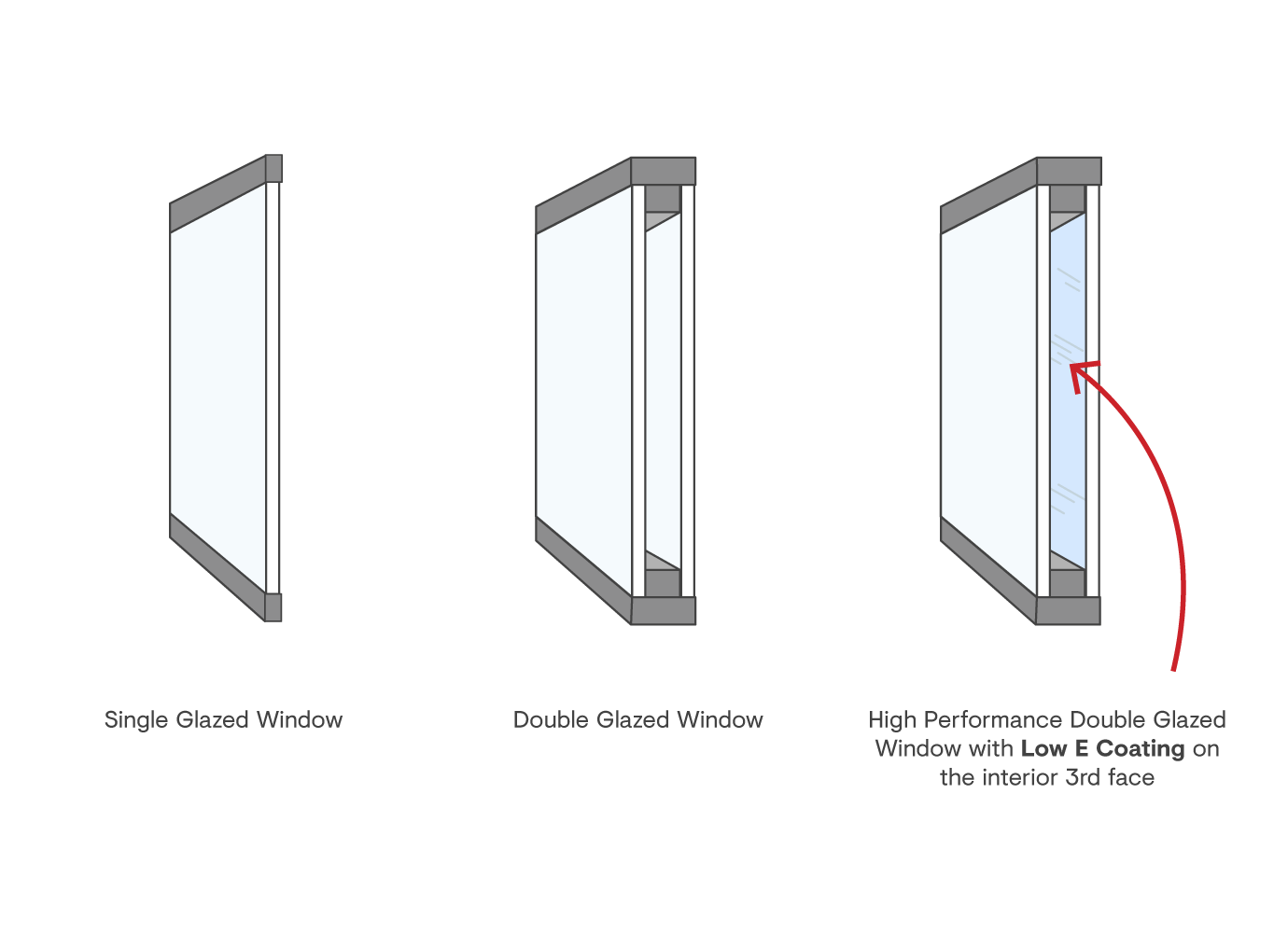
If you pick a window with half the U value (3. 1W/m2 C) (for example, double glazing with an argon-filled space and less-conductive frames), you can cut in half the heat loss: 3. 1 15 70 = 3255W The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) for windows (revealed as SHGCw) determines how readily heat from direct sunshine flows through an entire window (glass and frame together).
The lower a window's SHGC, the less solar heat it sends to your home interior. Glazing makers declare an SHGC for each window type and style. The actual SHGC for windows is affected by the angle that solar radiation strikes the glass. This is referred to as the angle of occurrence.
How To Retrofit Your Windows With Double Glazing, And Keep ... in Ferndale WA
When the sun is perpendicular (at 90) to the glass, it has an angle of incidence of 0 and the window will experience the optimum possible solar heat gain. The SHGC declared by glazing producers is constantly calculated as having a 0 angle of incidence. As the angle increases, more solar radiation is shown, and less is transferred.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Energy Efficient Windows At Everest in Lakes Perth
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in South Fremantle Western Australia
How Are Double Glazed Windows More Energy Efficient? in Safety Bay Western Australia
More
Latest Posts
Energy Efficient Windows At Everest in Lakes Perth
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in South Fremantle Western Australia
How Are Double Glazed Windows More Energy Efficient? in Safety Bay Western Australia